Khan Academy Economics Monopoly
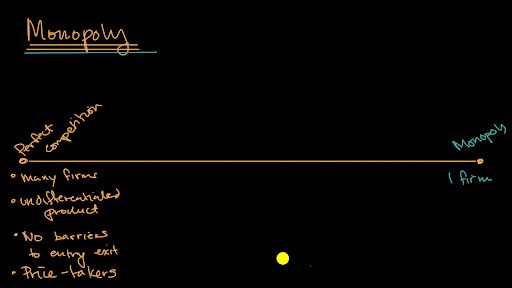
Belajar gratis tentang matematika, seni, pemrograman komputer, ekonomi, fisika, kimia, biologi, kedokteran, keuangan, sejarah, dan lainnya. Figure 10.3 “perfect competition versus monopoly” compares the demand situations faced by a monopoly and a perfectly competitive firm.
Economic Profit For A Monopoly Video Khan Academy
Khan academy adalah organisasi nonprofit dengan misi memberikan pendidikan kelas dunia secara gratis untuk siapa pun, di mana pun.
Khan academy economics monopoly. What are the 3 characteristics of a monopoly? Economic profit for a monopoly. Our interactive practice problems, articles, and videos help.
In panel (a), the equilibrium price for a perfectly competitive firm is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. Monopolistic competition and economic profit | microeconomics | khan academy. For example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic.
Learn more about the economic and financial implications of monopolies existing within any business sector. Marginal cost, average cost and marginal revenue. In the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share.
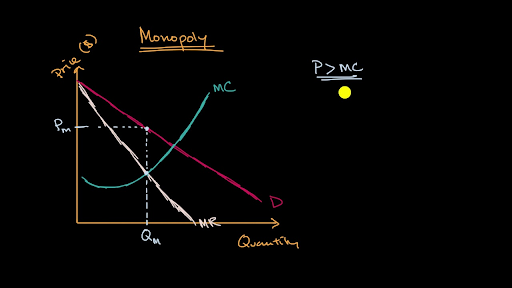
(opens a modal) monopolist optimizing price: Learn about some of the key ideas that influenced early economic thinkers, such as adam smith, in this video.practice this yourself on khan academy right now. Because a monopoly firm has its market all to itself, it faces the market demand curve.
Topics covered in a traditional college level introductory macroeconomics course. Increasing opportunity cost | microeconomics | khan academy. (opens a modal) monopolies vs.
Supply, demand, and market equilibrium. (opens a modal) marginal revenue and marginal cost in imperfect competition. Learn about how to represent a monopoly market graphically in this video.
Khan academy with this free online course in understanding monopolies, you about market situations where one producer or a group of producers acting in concert controls the supply of a. Practice what you have learned about the sources of monopolies and how a monopolist makes quantity and pricing decisions in this exercise. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e.
Microeconomics is all about how individual actors make decisions. Learn about how to represent a monopoly market graphically in this video. (opens a modal) economic profit for a monopoly.
Monopoly characteristics include profit maximizer, price maker, high barriers to entry, single seller, and price discrimination. Monopoly basics | forms of competition. Types of competition and marginal revenue.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Learn how supply and demand determine prices, how companies think about competition, and more! Review of revenue and cost graphs for a monopoly.
Difference between every day and economic notions of investment and consumption watch the next lesson:

Monopoly Basics Monopoly Khan Academy Basic
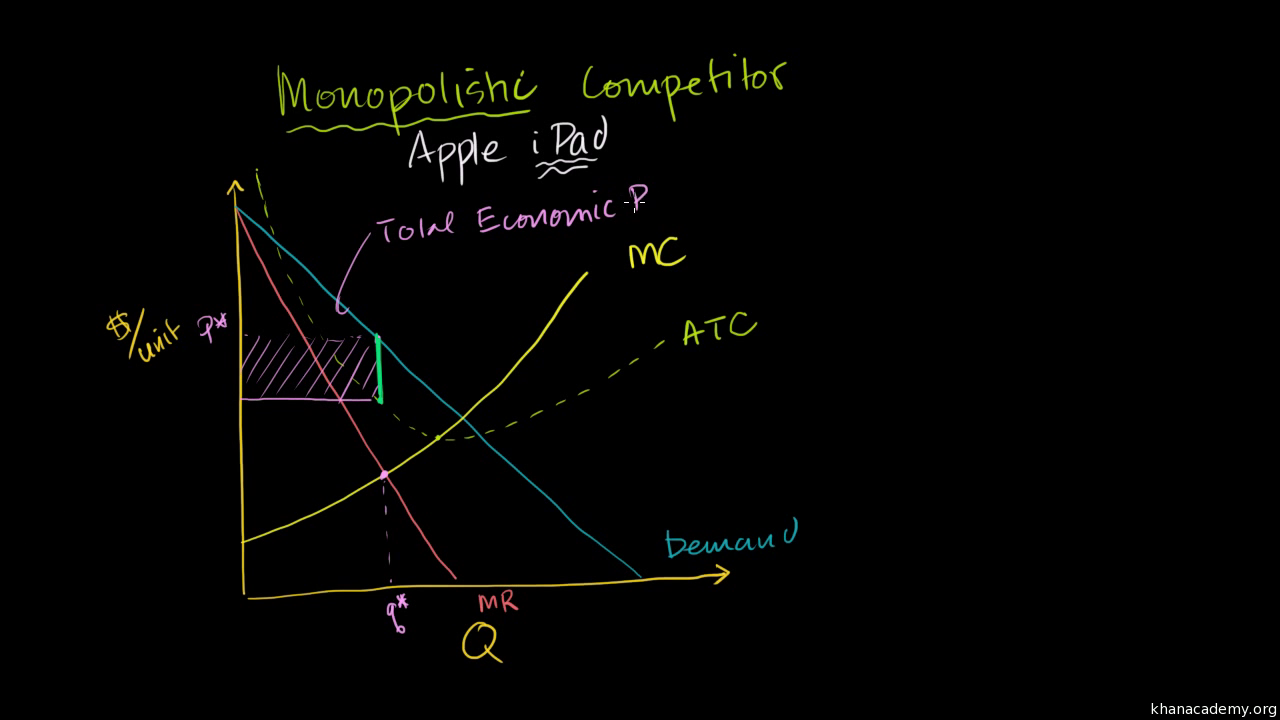
Monopolistic Competition And Economic Profit Video Khan Academy

Natural Monopoly Microeconomics I A Level And Ib Economics - Youtube
Videolecturenotesa11
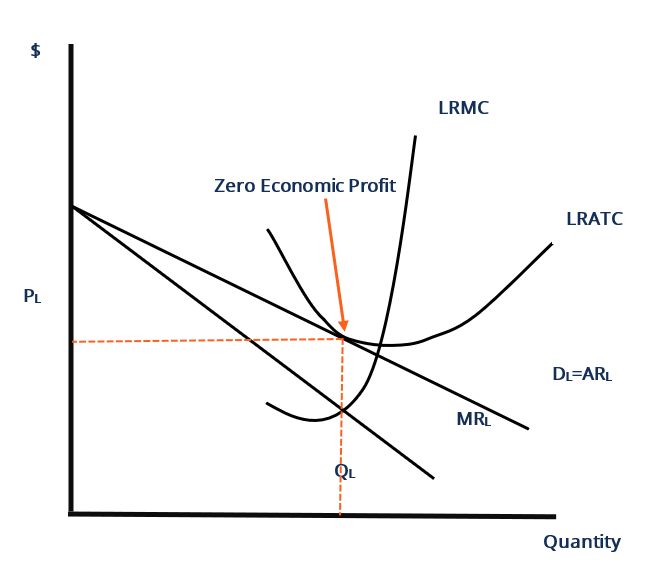
Orvosi Megereszkedese Orgyilkossag Long Run Profits In Monopoly And Oligopoly - Atsnobilitynoidaextensioncom

410 Monopoly Vs Perfect Competition Ap Micro - Youtube

Graphing A Monopoly Looks Similar To The Grand Daddy Graph This Shows How To Graph A Monopoly Graphing Monopoly Macroeconomics

Perfect Competition Ap Microeconomics Crash Course Review Httpswwwalbertioblogperfec Perfect Competition Teaching Economics Efficient Market Hypothesis
Monopolies Vs Perfect Competition Video Khan Academy
Micro Video Lecture Notes

Khan Explaining Monopoly Perfect Competition Monopoly Book Publishing
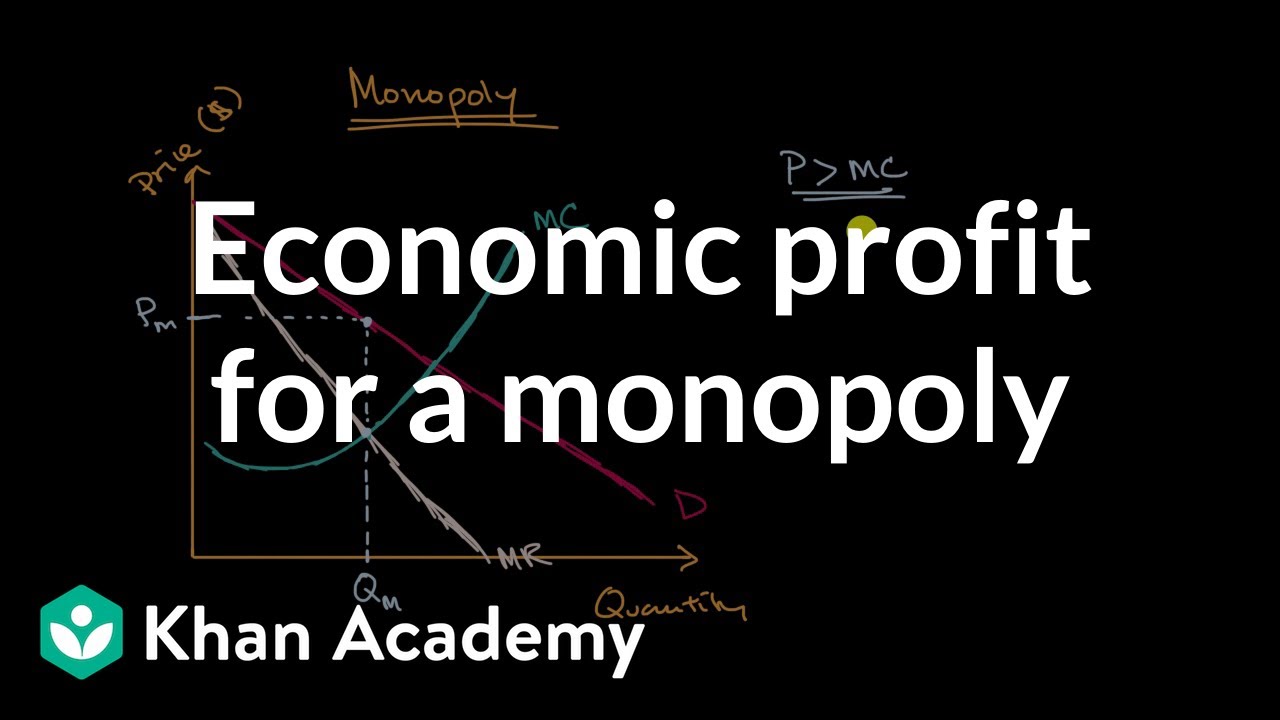
Economic Profit For A Monopoly Video Khan Academy
Modules
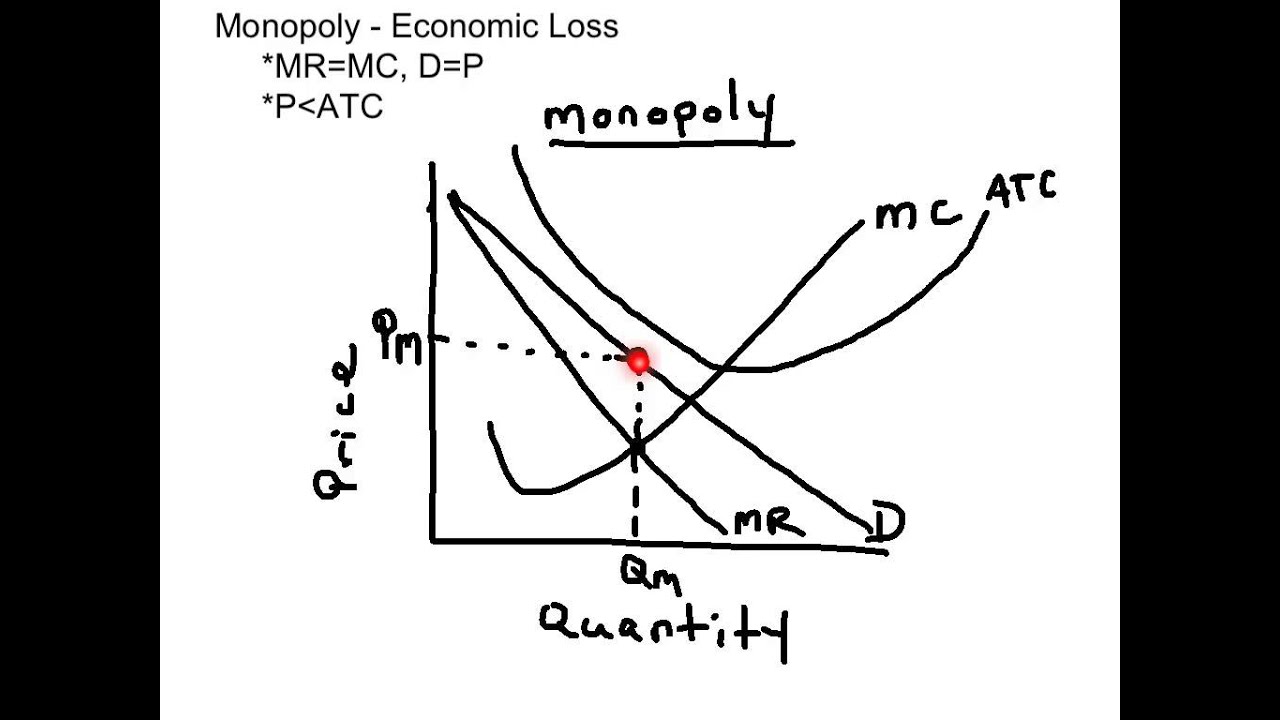
Monopoly Economic Loss Graph - Youtube
Modules
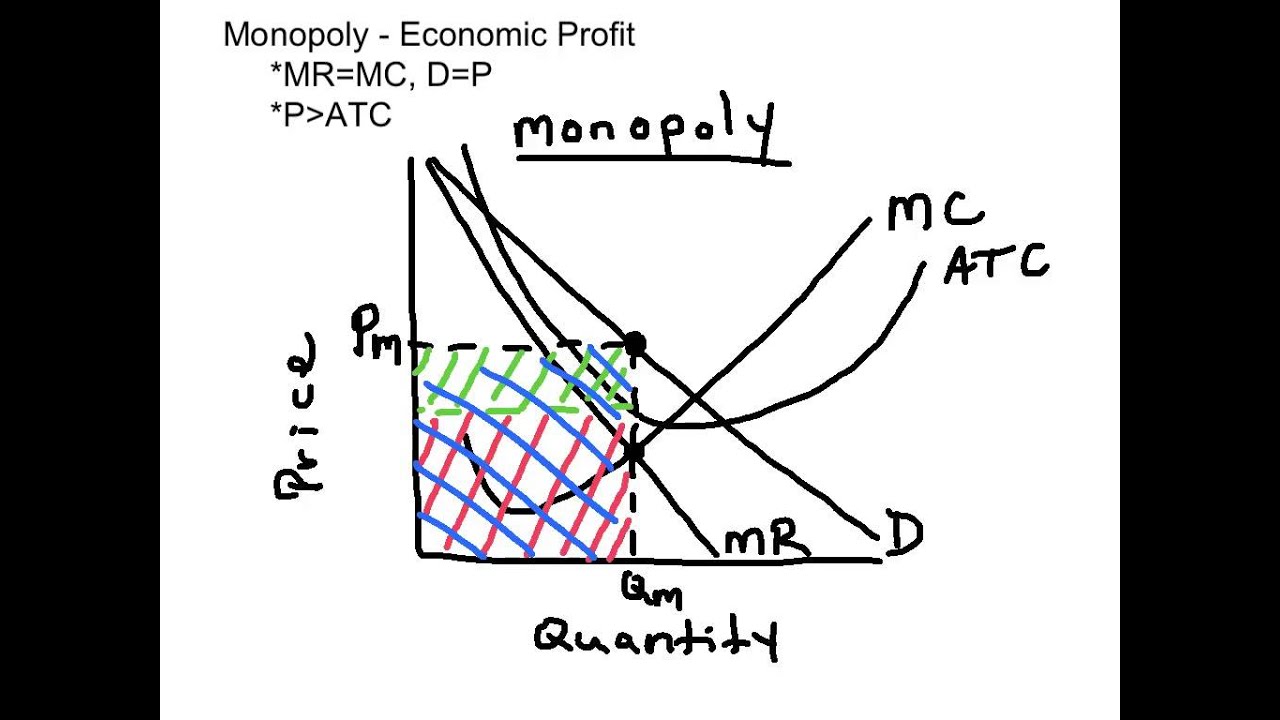
Monopoly - Economic Profit - Youtube

Monopolistic Competition Economic Profit - Youtube
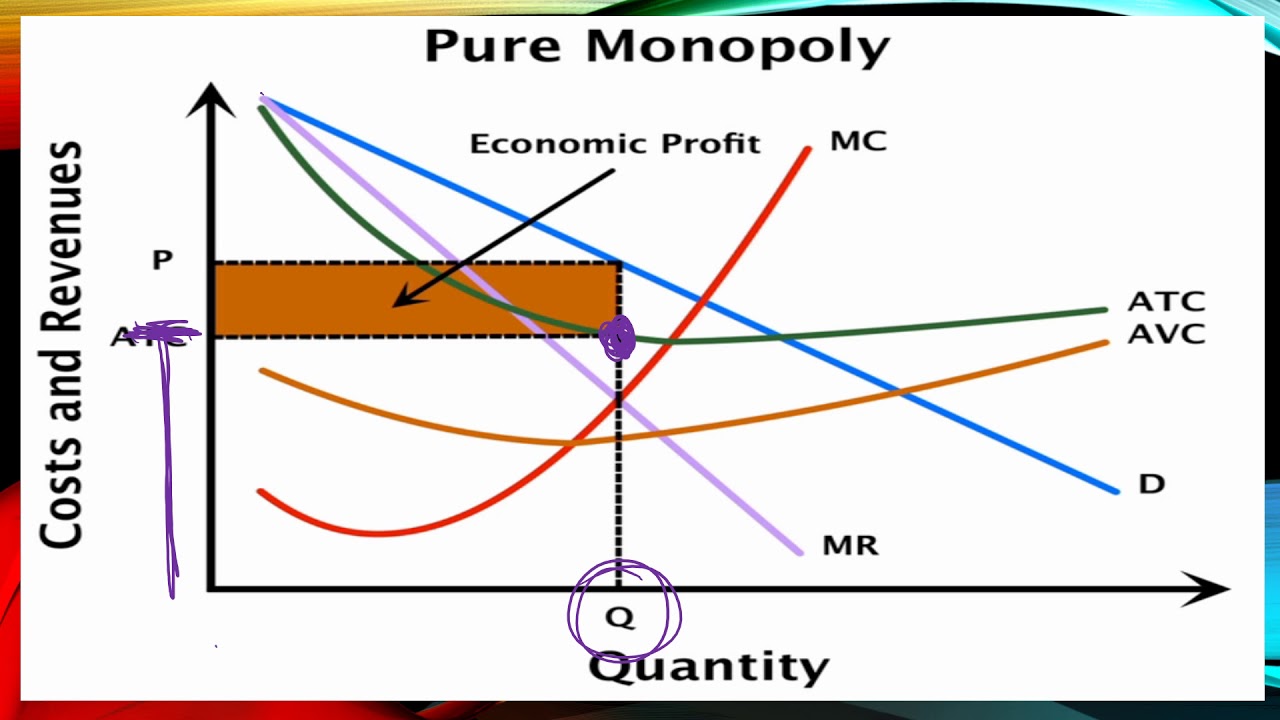
Market Power - The Monopoly Graph - Youtube
Modules